| Lægegerningen

| | Æbelholt Kloster udviklede sig i løbet af middelalderen til et betydeligt center for bekæmpelse af sygdomme.
Udgravninger fra 1930´erne dokumenterer munkenes kunnen og giver et godt indblik i middelalderens sygdomsbillede. |
Medicinsk center
Omfattende udgravninger på Æbelholt Klosters grund har først og fremmest givet et billede af klostret som et medicinsk center i Nordsjælland. Abbed Wilhelm anvender selv et sted betegnelsen hospitalsbrødrene og lægegerningen skal ses i sammenhæng med klosterets grundliggende funktioner som center for sjælsfrelse og siden hen valfartssted.
Æbelholts beliggenhed i tilknytning til det tættest befolkede område i Nordsjælland, Jørlunde Herred, og den meget direkte tilknytning til Hvide-slægten kan måske medvirke til at forklare lægegerningens fremtrædende rolle.
Klostrets ledingspligt
I modsætning til Esrum Kloster havde Æbelholt ledingspligt, selvom man i lange perioder betalte sig fra det. Det ældst kendte bevis herpå stammer fra 1251, hvor kong Abel fritager ”klosteret kannikker, bryder, landboer og ejendom for leding, ombudsmandens krav og alle andre afgifter til kongen”. Til trods for disse fritagelser tyder undersøgelser af skeletter fra Æbelholt på områdets tilknytning til den militære organisering. Påfaldende mange af de helbredte og ikke-helbredte skader er hugsår og andre krigsskader, og det antages at en fremtrædende del af de begravede har haft tilknytning til militærvæsenet, måske som ledingspligtige fribønder.
Skelet | 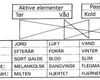
De fire elementer |
Sygdomslæren
Middelalderens lægevidenskab udvikler sig fra omkring slutningen af 600-tallet i forbindelse med Salerno-klostrets lægeskole i Syditalien, hvorfra der udgik talrige medicinske og kirurgiske værker. Salernoskolen byggede på den klassiske tids hippokratiske lære om legemets fire væsker: Blodet i årerne, slimet(flegma) i hjernen og lungerne, den gule galde i leveren og den sorte galde i milten. Til disse væsker var knyttet forskellige egenskaber: Blodet var varmt og fugtigt, slimen kold og fugtig, den gule galde varm og tør og den sorte galde kold og tør:
Som det ses af modellen indgår sygdomsopfattelsen i tidens kosmologiske helhedsopfattelse, som relaterer sig til den såkaldte elementærlære om de fire elementer(jord, luft, vand og ild), der omfatter den kendte verden: Endvidere kunne legemets enkelte dele sættes i forbindelse med dyrekredsen stilling på stjernehimmelen og danne udgangspunkt for anvendelsen af åreladninger, hvor man regulerede på væskebalancerne i overensstemmelse hermed.

De fire elementer |
Urtemedicinen
Sygdomsforståelsen går endvidere ud på at der eksisterer en balance imellem de fire legemsvæsker, at sygdom skyldtes en vis ubalance, som man så forsøgte at rette op på. Gennem undersøgelse af urin og puls kunne lægen bestemme ubalancen og anvende medikamenter med modsat virkning. Disse medikamenter var bl.a. urter som man dyrkede i klostrenes haver og som dannede baggrund for den udbredte anvendelse af urtemedicin i middelalderen.
Roskilde-kannikken Henrik Harpenstreng (1164-1244) bog om urtemedicin vidner om urtemedicinens udbredelse på vores breddegrader allerede i tidlig middelalder. Urterne der anvendes omfatter både mere eksotiske krydderier, såsom ingefær og muskat, men også planter der hører til i Norden(f.eks. Kvan) og det vi nu om dage vil kalde grøntsager, f.eks. rødløg og porrer.

Urtehaven | 
Kors-Vortemælk |
Kirurgiske indgreb
Særdeles omdiskuteret i samtiden var anvendelsen af kirurgiske indgreb, idet kirken forbød lægekyndige gejstlige at foretage kirurgiske indgreb med blodsudgydelse. I hele taget var det omdiskuteret om og i hvilket omfang man burde udøve lægegerningen. Den indflydelsesrige cisterciensermunk Bernard af Clairveaux mente, således som det fremgår af følgende citat, at "...det at konsultere læger og indtage medicin ikke gavner religionen og er i modstrid med renhed..."
Ikke desto mindre kan man konstatere at der f.eks. på Æbelholt Kloster er foretaget indgreb, som har forårsaget blodsudgydelse, bl.a. trepanering, hvor man har boret hul i kraniet, formodentlig for at lindre betændelsestilstande. Størstedelen af indgrebene i Æbelholt vedrører dog forskellige knoglebrud, som kan behandles uden kirurgiske indgreb, og sårbehandling på allerede forårsagede brud.

Skelet | 
Deform rygsøjle | 
Æbelholt Kloster | 
Trepanering | 
Instrumenter |
|