| Renæssance

| | Den verdensberømte videnskabsmand Tycho Brahes mange rejser mellem Skåne, Hven og København i 1500-tallets sidste halvdel er et markant eksempel på den intense kommunikation, der fandt sted mellem landsdelenene. |
Uranienborg på Hven
Renæssancefyrsten Frederik 2.havde blik for Tycho Brahes format og tilbød ham støtte og d.18.2.1576 tilstedes han en årlig udbetaling på 500 daler, en statsstøtte af dimensioner. Kongen havde under tilsyn med byggearbejdet på Kronborg fået øen Hven i tankerne, som et passende sted for Tycho Brahes virksomhed, og Tycho Brahe kunne få den som len på fordelagtige vilkår, hvis det kunne afholde ham fra at rejse til udlandet. Tycho Brahe accepterer kongens tilbud.
Ovenikøbet får Tyge 400 rigsdaler til opførelse af et hus på Hven. I august 1576 påbegyndes byggeriet af Tycho Brahes nye bolig Uranienborg, opkaldt efter himmelgudinden Urania. Det praktiske arbejde udføres som hoveriarbejde af øens bønder, og som ledere af byggeriet har man bl.a. foreslået to af de fra Kronborgbyggeriet kendte nederlandske bygherrer Hans von Paeshen og Hans van Stenwinckel. Selve byggeriet er inspireret af norditaliensk renæssance, som Tycho Brahe har stiftet bekendtskab med under sine udenlandsrejser, og der er næppe tvivl om, at han selv har bidraget til udformningen af byggeriet.
I vore dage er der ikke mere tilbage af slottet.
En symbolsk bygning
De centrale del af grundplanen udgøres af et kvadrat, der måler 60 fod, ca 15,5 meter på hver side. Dette kvadrat deles af vinkelrette korridorer, der deler grundkvadratet i fire ens mindre rum og endvidere forbinder symmetriske tilbygninger i nord- sydlig retning og ligeledes symmetriske indgangspartier i øst og vest.
Bygningen består af to etager, fuld kælder og en kvistetage. Uden påbygningen er tilføjet altaner til brug for observationer og en del af kælderen er beregnet til kemisk laboratorium. Astronomien og kemien/medicinen var de videnskaber man ville give sig af med og det angives tillige med to figurnicher over indgangspartierne. De allegoriske fremstillinger her har været knyttet sammen med nogle korte latinske inskriptioner: DESPICIENDO SUSPICIO og SVSPICIENDO DESPICIO, hvilket betyder noget i retning af: Idet jeg ser ned skuer jeg opad, og idet jeg ser op, skuer jeg nedad.Den første sentens er møntet på de kemiske eksperimenter, den anden refererer naturligvis til de astronomiske studier.

Uranienborg | 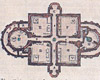
Grundplanstegning |
Kosmologien
Den dybere mening med Tycho Brahes valgsprog er, at de videnskabelige studier har kosmologisk sammenhæng, at der er indbyrdes forbindelse imellem studiet af de jordnære ting og det guddommelige og at studiet af planetsystemets opbygning har relation til den jordiske tilværelse.
Uranienborg var således ikke alene hjem og arbejdssted for Tycho Brahe, men udtrykte tillige arkitektonisk og på anden vis den livsopfattelse og verdensanskuelse, der ligger til grund for Tycho Brahe og mange andre renæssancehumanisters arbejde og virke: En tro på at udforskning og kortlægning af virkeligheden vidner om den kosmologiske sammenhæng, der ligger bag.
Havekunst og medicin
Det samlede kompleks omkring Uranienborg viser igen det sammenhængende og symmetriske, her i haveanlægget og de omgivende voldanlæg. Haveanlægget er et af renæssancens interesseområder, men her har det også tjent mere praktiske formål, idet træerne også var frugttræer og bedene rummede såvel grøntsager, som urter, der også kunne indgå i medicinske opskrifter.
Vi ved at både Tyge og hans lærde søster Sophie Brahe, der i lange perioder opholdt sig på Hven, gav sig af med at fremstille medicinske præparater, endda i et sådant omfang, at apotekerne i København klagede over det. Det er sandsynligt, at Sophie Brahe har deltaget i anlæggelse og pleje af haveanlægget, men sikre beviser for det har vi ikke.

Have- og voldanlæg | 
Grundplan |
Tycho Brahe forlader Hven
Tycho Brahe bliver på Hven i 21 år, frem til 1597, hvor han falder i unåde og nødtvungent forlader Danmark og i 1599 slår sig ned i Prag, hvor han dør i 1601. Omstændighederne omkring Tycho Brahes fald er fortsat uklare og omdiskuterede. Fra Rostock skriver Tycho Brahe i 1597 selv til kongen, at han ikke er draget i eksil og forsikrer om sin fortsatte loyalitet. Kongen bebrejder ham, at han er drager bort uden tilladelse ogpå peger uoverensstemmelser, idet han henviser til "Klagemaal vore fattige Undersaatter og Bønder paa Hven imod dig haver haft" og hans forsømmelighed mod kirken sammesteds, herunder "Udi hvad Maade Daabsens Ord ere udi langsommelig Tid udeladte, imod disse Rigers vedtagne Brug, med dit Vidskab, sligt er hver Mand altfor vitterligt."
At Tycho Brahe ikke overholdt sine lensforpligtigelser til punkt og prikke er en kendsgerning, han forsømte at passe fyret på Kullen og værre endnu det kongelige gravkapel i Roskilde Domkirke. Det kan imidlertid undre at stridsmålet med bønderne drages frem i en tid, hvor det er enhver herremands ret at udnytte sine undergivne og hvor byrden på bønderne generelt set øges betydeligt.
Buxtehude - en øresundsborger
I årene 1638-41 virkede Buxtehude den ældre i Helsingborg og her tilbragte Diderik nogle barneår. I 1642 fik faderen tjeneste som organist ved Skt. Olai Kirke i Helsingør, hvor han var aktiv frem til 1670. Barne- og ungdomsår tilbragte Diderik Buxtehude altså både i Helsingør og Helsingborg.
Rigt musikliv
I 1600-tallet første halvdel var musiklivet ved det danske hof og i de større kirker af meget høj klasse. Navne som Heinrich Schütz og John Dowland er gået over i musikhistorien. Schütz var kirkemusiker i Købehavn og opbyggede hofkapellet der. Dowland, berømt lutspiller og komponist, var hofmusiker og holdt til i Helsingør. Johann Lorentz virkede i første halvdel af 1600-tallet som kongelig orgelbygger og byggede, eller ombyggede alle vigtige orgler i Øresundsregionen i en da ganske konservativ renæssansestil som da repræsenteredes af Heinrich Schütz og John Dowland. Et af de vigtigste vidnesbyrd om Lotrentz virksomhed findes i orgelfacaden på Chrisstiansstads Trefoldighedskirke.
Organist tur-retur
Diderik Buxtehude gik i sin fars fodspor og blev i 1657 organist i Mariakirken i Helsingborg. 1660 søgte han og fik organistembedet ved Mariakirken i Helsingør. Formodentlig fordi dette embede var bedre lønnet og han dermed kom tættere på resten af familien. I tiden frem til 1668, hvor Buxtehude drager til Lübeck og søger embede der, bor han således i samme hus som faderen og moderen. Huset findes endnu i Helsingørs Skt. Annægade.
Samtidig skede der en modernisering af de gamle Lorenzorgler til en moderne barokstil, en stil som repræsenteres musikalsk af Diderik Buxtehude. Den nordtyske orgelbygger Hans Christoff Frietzsch stod for denne modernisering og han var manden bag om- og nybygning af orgler i København, Helsingør, Halmstad, Helsingborg, Landskrona og Malmö.
Diderik Buxtehude oplevede altså og deltog i en meget aktiv fornyelse af musiklivet gennem de nybygninger som foretoges. To år efter han var flyttet til Helsingør vendte han tilbage til Helsingborg(1662) for at føre tilsyn med ombygningen af orglet i Mariakirken. Dette tyder på at den svenske magtovertagelse af Skåne i 1658 ikke umiddelbart påvirkede musiklivet.

Mariakyrkan i Helsingborg | 
Sct. Annægade i Helsingør | 
Det gamle orgel | 
Buxtehude | 
Kororgel i Mariakyrkan |
Forbindelsen opretholdes
I sin tid i Helsingør opretholder Buxtehude også tætte forbindelser til både danske og svenske embedsborgere. Det eneste med fuldt sikkerhed kendte musikstykke som Buxtehude har skrevet i sin tid i Helsingør er således i året 1665 tilegnet Christoffer Schneider, der var svensk postmester og senere kommisarius bosiddende i Helsingør. Ligeledes havde Buxtehude allerede fra Helsingør-tiden venskabelige forbindelser med den svenske hofkapelmester og organist Gustav Büben. Måske er det også på hans foranledning at Buxtehude i 1680 komponerer bryllupskantaten til brylluppet imellem Karl 11.Gustav og hans danskfødte dronning Hedvig Eleonora.
| |
 | | Stor | Aperte mihi portas justitiae, Helsingør 1665 (Diderik Buxtehude) |
 | | Stor | Aria sopra le Nozze di Sua Maesta il Re de Svecia (1680) (Didrik Buxtehude) |
Tiden i Lübeck
1668 flyttede Diderik Buxtehude til Lübeck, formodentlig af hensyn til sin fortsatte karriere, men nok også for at komme væk fra de trange økonomiske vilkår i den krigshærgede Øresundsregion. Som en rød tråd i Buxtehudes liv går de tre mariakirker i Helsingborg, Helsingør og Lübeck. Selvom størstedelen af hans aktive liv var forlagt til Lübeck og selvom han der vandt den største ære og berømmelse, så glemte han aldrig sine rødder ved Øresund. Derfor kunne tidsskriftet Nova litttraria Maris Balthici år 1707 påstå, at ”han anså Danmark for sit fædreland” (Patriam agnoscit Daniam).
Diderik Buxtehudes karriere som komponist og organist kulminerede i Lübeck, hvortil storheder som Händel og Bach vandrede for at lytte til hans musik. Det var som organist og komponist i Mariakirken i Lübeck han vandt sin store berømmelse. Især var han kendt for sine ”Lübecker Abendmusik” som var koncerter i tilknytning til aftensangen søndagene før jul. Til disse skrev han hvert år et nyt orgelværk. |